When a computer boots, something takes place in the background that precedes even the start up of the operating system. This is unobservable and it is governed under the BIOS (Basic Input Output System), or in the newer systems, the UEFI firmware. Although inaccessible to the majority of computer users, the BIOS defines how your PC starts up successfully, identifies hardware and interacts professionally with other devices.
To check the Bios versio Press Windows + R keys. Type msinfo32 and hit Enter. In the System Information window, check under System Summary. Look for the entry labeled BIOS Version/Date.
In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss how to find out the version of BIOS on many systems, why updating matters and why it can present some risks. By the end you will not only know how to find your version but also why it may just be a savior in the PC maintenance field.
Understanding BIOS and UEFI
Terminology The following terms are commonly used when discussing versions. Conventional BIOS has been in existence since the early 1980s. It is a small software that resides on a chip in your motherboard model and serves to initialize the hardware in the startup process.
Most current personal computers have UEFI and not BIOS. Unlike BIOS, UEFI supports the bigger hard drives, faster boot up and also provides a more user friendly interface. Even though it is not the exact same thing as BIOS, due to the similarity, people tend to refer to it by the same name, so do not get confused in case your system runs UEFI.
What you can see on the check of your version may be either BiOS or UEFI. The methods used to check are the same only that the terminology may vary a bit.
Why Knowing Your BIOS Version Matters
A good portion of PC problems can be attributed to out of date firmware versions. Suppose there are following scenarios:
- You remove the old graphics card and mount a new one but the system fails to start.
- Random failure of Windows which often recurs after a fresh Installation of PS2 BIOS.
- Security researchers determine a vulnerability of some BIOS builds.
In each of the cases, it is the BIOS version that becomes the most important clue. Here’s why:
- Hardware compatibility: New CPUs or RAM modules will have an new BIOS support requirements.
- Stability of old versions: This could lead to boot problems with old versions as they might already have bugs in them.
- Security patch: Since as with OS, BIOS may be vulnerable.
- Better performance: The Updated BIOS software will allow faster booting, and internal hardware communication can also be made more smooth.
In brief, the info about your BIOS version will be beneficial to you. It is as when you have acknowledged the basis of your house then you add more floors.
5 Easy Methods to Check BIOS Version
You can find your BIOS version in a number of ways. They include some graphical, as well as some command line, and even third party tools. So, let us review them one after another.
1. Using Windows System Information Tool
This is the easiest method for Windows users.
Steps:
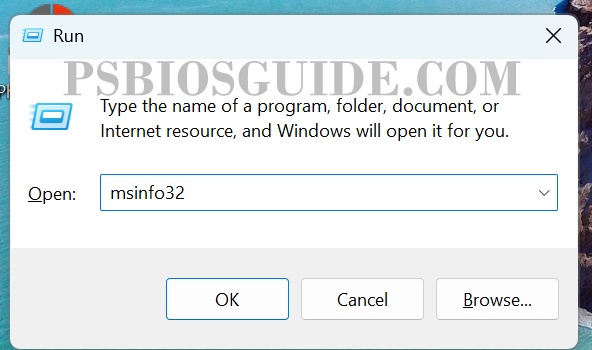
- Press Windows + R keys.
- Type
msinfo32and hit Enter. - In the System Information window, check under System Summary.
- Look for the entry labeled BIOS Version/Date.
Example output:
American Megatrends Inc. 3.70, 07/15/2021
This tells you both the BIOS manufacturer and the release date.
2. Checking BIOS in Command Prompt
For people who prefer a lightweight method:
- Open Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Type: wmic bios get smbiosbiosversion
- Press Enter.
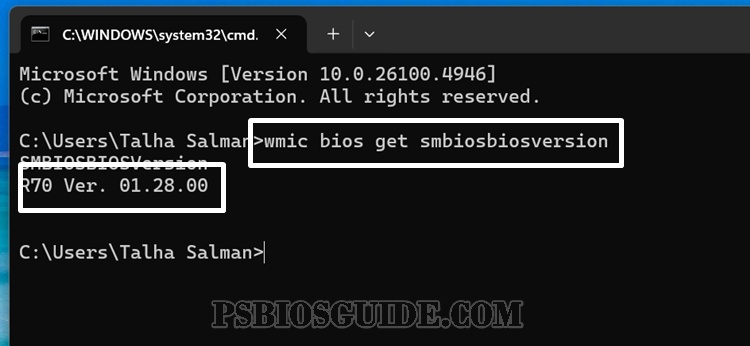
This will display the firmware version instantly. It’s fast, reliable, and works on all Windows builds.
3. Checking BIOS via PowerShell
Another robust option is PowerShell, which provides more details.
Command:
Get-WmiObject win32_bios | Format-List
This command outputs:
- BIOS version
- Manufacturer
- Serial number
- Release date
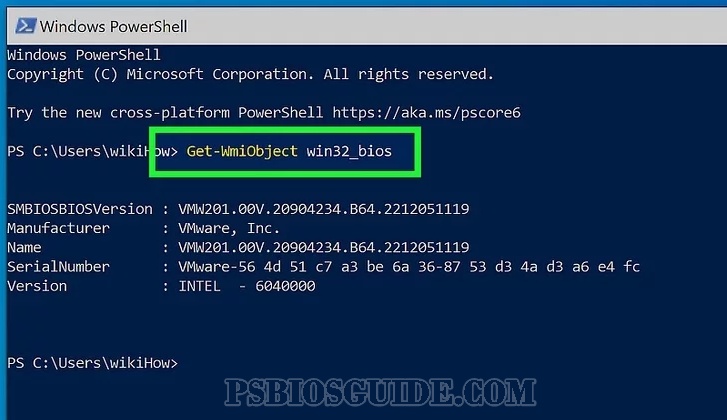
This method is especially useful for IT administrators who need to gather details across multiple machines.
4. Checking BIOS During Startup
If you want direct confirmation straight from the source, restart your PC.
- As the system powers on, press Del, F2, or sometimes Esc (depends on your motherboard).
- You’ll enter the BIOS setup utility.
- The version is usually displayed on the main page.
This method bypasses the operating system entirely, making it useful if Windows won’t boot.
5. Using Third-Party Tools
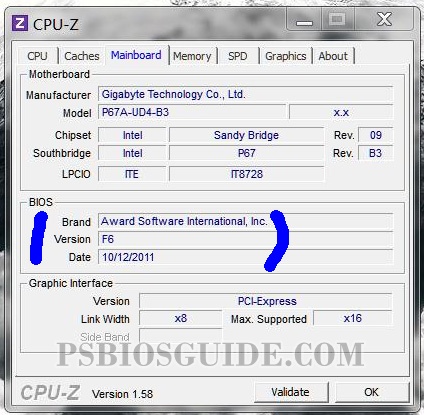
Applications like CPU-Z, Speccy, and AIDA64 provide extended system information. These tools don’t just show BIOS details but also CPU type, RAM configuration, and even boot menu settings.
For example, in CPU-Z, you’ll find a “Mainboard” tab. Under it, the BIOS version and date are displayed alongside the motherboard vendor.
How to Interpret BIOS Version Numbers
As they seem at the first glance certainly cryptic strings like F.23 Rev.A or 3.70 still indicate particular song or liturgical books, particularly since the first has a period in it and the second is an even number. But the following will decode them:
- Manufactuer prefix: Identifies the maker (e.g. American Megatrends, Phoenix).
- Release: Displays the iteration of the release. The higher the more recent releases tend to occur.
- Confirm: The release date of the build.
When making a comparison between your version and the one that is on the manufacturer site, check the number and release date.
When Should You Update BIOS?
The golden rule is updated when it is necessary.
Update if:
- Upgrades (e.g. to newer CPUs).
- Having a problem of stability
- Notes on release by manufacturer indicate the fix to your problem.
Do not update unless:
- Your system is sound
- You do not require the new hardware support.
BIOS updates are risky as opposed to normal software. Should they be cut off, the motherboard can fail to boot properly.
Precautions Before Updating BIOS
To be on the safe side, one should adhere to the following precautions before an attempt to upgrade his BIOS:
- backup critical files
- Disconnect peripherals such as USB drive and printers.
- Get a steady power supply, do not update when there is a storm or your battery is low.
- Stay with the sources of updates.
Troubleshooting BIOS-Related Issues
Occasionally, it is not enough to check the version. You can have problems such as:
- Hanging at the boot screen
- Poor reporting of the hardware configurations
- Missing boots in boot menu
In case this occurs, check your firmware against the most current at the manufacturer site. A patch might also be the solution, in case you are several versions out of date.
Real-World Scenarios
CPU Upgrading A user upgrades his/her CPU to Ryzen, and the system fails to boot. Solution? Prompted by installing BIOS will allow support of the chip.
- Security Fix: Intel reports the flaws in older versions of BIOS. Manufacturers patch Version checking protects you
- Slow Startup: There are times when new BIOS versions optimize the boot up. The verification of your version also determines whether an update is worthwhile or not.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I check BIOS version on Linux?
Yes. Run:
sudo dmidecode -s bios-version
Is BIOS the same as UEFI?
Not exactly. UEFI is newer, more advanced, but serves the same purpose.
What happens if BIOS update fails?
In worst cases, the motherboard may not boot. Some modern boards include a recovery feature, but not all.
Can BIOS affect performance?
Yes, particularly in boot speed and hardware efficiency.
Conclusion
It is not only a technical curiosity to check your version of the BIOS. It is one of the most important things in keeping a stable, secure, and compatible PC. To get the information, you can use Windows programs, such as System Information or PowerShell, the command line, or third-party programs, such as CPU-Z, and you need to go through only a few steps to get the job done.
BIOS update can be strong and dangerous. Nevertheless, compatibility should always be confirmed, instructions of the manufacturers should be followed and the process should not be interrupted.
Now you can troubleshoot with intelligence, make the necessary upgrade without worry and keep your system functioning at optimum capacity.

