Navigating the inner layers of your computer isn’t always the simplest task, yet sometimes it’s necessary. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is one of the most important regions that you may need to enter. Regardless of the problem you are trying to troubleshoot a hardware or alter the preferences in the boot, or virtualising software to use, knowing how to enter BIOS in an operating system is a mandatory skill in Windows 10 and 11.
There are explanations, step-by-step techniques and background information that you will find helpful in this guide. At the end, you are not only going to know how to get to BIOS, but also why it can be so important to do so to ensure the performance and security of your system.
What Is BIOS and Why Does It Matter?
Now let us pause momentarily to the what before we sink into the how. BIOS Abbreviation Basic Input/Output System, is a small program that is on a chip on your motherboard. It has a simple but mighty task, to boot up your system, test hardware and handover control to the operating system. BIOS is frequently substituted or supplemented in the modern computers by UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface).
Why should you care? Since it is the place where you set low-level settings. As an example, you can swap the boot sequence, turn on Secure Boot, lock a PS2 BIOS password, or adjust overclocking settings. All these modifications are able to have an immediate effect on the behavior of your PC.
When When Do You Need to Enter BIOS?
BIOS is not touched by all users, however, certain situations necessitate it:
- Changing a hard drive or SSD and modifying a boot order.
- Allowing the use of virtualization technology to execute virtual machines.
- Diagnose hardware issues such as detection of RAM problems.
- Control of fans or thermal controls to achieve greater cooling.
- Restoring the system passwords or erasing forgotten setting.
- Switching off Secure Boot to install different operating system.
BIOS in brief is the control room of your computer. In order to optimize or repair it deeper, you are required to enter PCSX2 Emulator.
How to Enter Bios Windows 10? (3 Methods)
Windows 10 gives multiple methods to access BIOS. Let’s explore them one by one.
1. Using the Restart Method (Shift + Restart)
This is the most user-friendly approach.
- Click on the Start menu.
- Select Power.
- Hold down the Shift key, then click Restart.
- Your PC will boot into the Advanced Startup Options menu.
- Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Finally, click Restart.
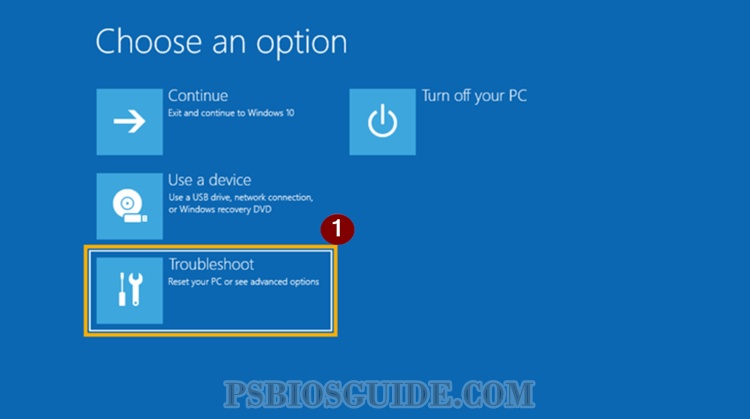
Your machine will reboot directly into BIOS. This method is especially handy because you don’t need to guess the right key during startup.
2. Using Settings in Windows 10
Another straightforward path:
- Press Windows Key + I to open Settings.
- Navigate to Update & Security.
- Click Recovery on the left panel.
- Under Advanced Startup, hit Restart Now.
- Follow the same steps: Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
This route is useful if you’re already inside Windows and want a seamless reboot into BIOS.
3. Using Startup Key (Manufacturer Keys)
Many users prefer the traditional method: pressing a key during startup. Common keys include F2, Del, Esc, or F10. The exact key depends on your motherboard manufacturer.
For example:
- Dell often uses F2.
- HP typically uses Esc or F10.
- ASUS might require Del or F2.
- Lenovo often uses F1 or F2.
Timing is critical you need to press the key right after the system powers on, before Windows starts loading.
How to Enter Bios Windows 11 (3 Methods)
Although Windows 11 looks and feels different, the BIOS entry process remains very similar.
1. Entering Through Settings
- Open Settings with Windows Key + I.
- Navigate to System > Recovery.
- Under Advanced Startup, select Restart now.
- After reboot, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Select Restart.
2. Using Shift + Restart
The process mirrors Windows 10:
- Hold Shift while selecting Restart.
- Move through Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.
- Restart into BIOS.

3. Manufacturer Keys
Just like Windows 10, pressing the dedicated BIOS key during startup works. What’s different is that Windows 11 boots faster, meaning you may need to be quicker at pressing the key.
Common Issues When Entering BIOS
At times, even with the best of your efforts you are unable to get in. Here are problems and fixes:
- The computer boots in a hurry: Use the windows settings method rather than the startup key.
- Key is wrong: Read your PC manual or on the manufacturer site.
- Fast Boot: Turn on Fast Boot in windows power settings, reboot and enable.
- Wireless keyboard is not recognized at first: Use a wired keyboard to get into BIOS.
Understanding UEFI vs BIOS
As stated above, a lot of contemporary systems have UEFI replacement with the regular BIOS. The terms can be used interchangeably though there are differences:
- UEFI supports larger hard drives, faster boot times, and a more graphical interface.
- BIOS is older, but still operational, and in text form.
When you select Enter BIOS on a Windows 11 computer, you are most likely to get into UEFI firmware.
Safety Tips When Modifying BIOS
When you are inside it is tempting to change every setting like as BIOS Version, but caution counts.
- Document your changes: Write down original values before modifying.
- Don’t make useless tweaks: It is not necessary to switch off security features unless you have a reason.
- Install BIOS cautiously: Do not use home-made tools; an unsuccessful update can lock up your machine.
- Restart: You can restart BIOS in default settings in case of any problems.
Advanced BIOS Options You Might Explore
After you feel at home with the BIOS, there are features to be familiar with:
- Overclocking: Overclock CPU or Overclock RAM.
- Control of boot order: Choose to boot off USB, off HDD, off SSD.
- Secure Boot: Protect against unauthorized operating systems.
- Virtualization (VT-x/AMD-V): Enable for virtual machine software.
- Speed control of fans: Silence or enhance cooling.
Performance can be enhanced with these settings, but it is also risky. Knowledge and not guesswork.
Troubleshooting BIOS Access in Windows 10 and 11
When all the methods fail, here is a step-by-step technique about Update BIOS:
- Check documentation: There is a key and a process of each brand.
- Turn off Fast Startup in Windows: Open the Control Panel and then Power Options and Select what the power buttons do and then uncheck Turn on fast startup.
- Use Command Prompt: shutdown /r /fw to boot in to firmware settings.
- Install system drivers: The system drivers can be old and prevent access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is BIOS the same as UEFI?
Not exactly. The newest variant of BIOS is called UEFI which has additional features and is also able to boot quicker.
Is it possible to destroy my computer by getting into BIOS?
No. It is just safe to enter BIOS. The only danger is to make changes without having knowledge of the critical settings.
What will happen in case I lose my BIOS password?
It might be required to clear the CMOS battery by resetting the battery (or jumpering on the motherboard).
What is the key to press?
Observe the screen when starting; it may tend to flash Press F2/Del to enter set up. Otherwise, consult the support page of your manufacturer.
Conclusion
It is more than a simple press of a key to know how to enter BIOS in Windows 10 and 11, it is knowing the importance of firmware, the various access points, along with the dangers presented. Having the above-described methods, you can be sure that you will enter BIOS regardless of whether you are on a current UEFI interface or a legacy setup screen.
Do not forget to be careful in BIOS. Although it paves way to customization and optimization it requires responsibility. Note taking, intentional amendments and always have a backup plan. Learning to do this, you are not only a user of your PC, but a commander of its inner life.

